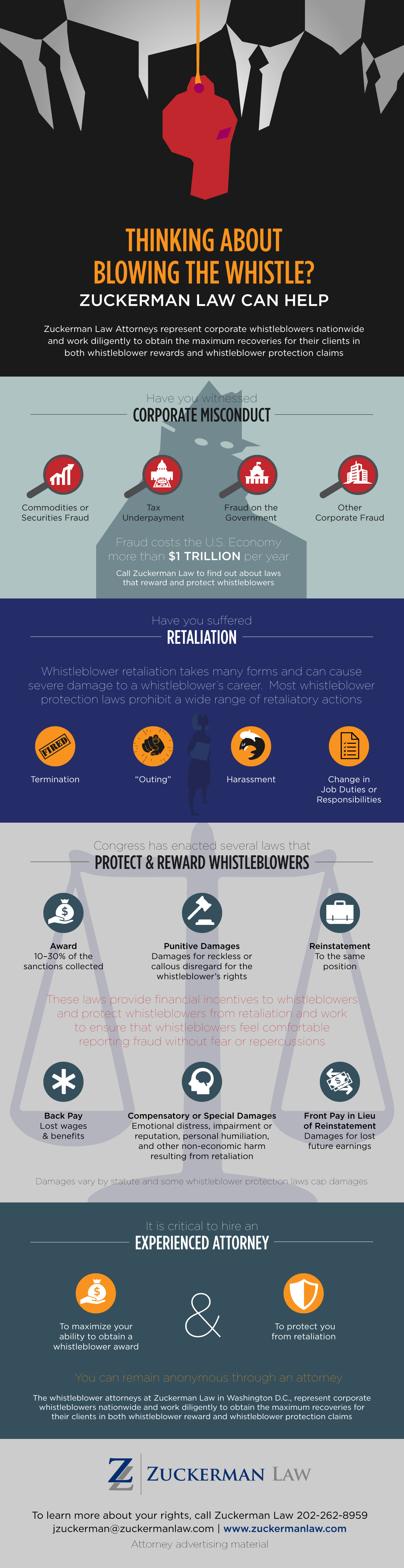
IRS Whistleblower Office Issues $120 Million in Awards in FY 2019
The IRS Whistleblower Reward Program recently released its annual report, which reveals that in FY 2019 the IRS made awards to whistleblowers exceeding $120 million and collected more than $616 million in proceeds as a result of whistleblower tips. While this represents a significant decrease in awards and collected proceeds compared to FY 2018 (when the IRS issued more than $312 million in awards and collected $1.4 billion in proceeds), it nevertheless appears that the program is headed in the right direction. Since the inception of the IRS Whistleblower Reward Program, the IRS has issued more than $931 million in awards to whistleblowers based on the collection of $5.7 billion. In the past two years alone, the IRS has issued nearly 47% of the total whistleblower awards to date.
In FY 2019, the IRS Whistleblower Officer experienced a decrease in tips received (11,394 tips) compared to FY 2018 (12,286 tips) and FY 2017 (13,3996 tips). Despite this decrease, the average time to process an award under § 7623(b) increased to 10.31 years in FY 2019, compared to 7.32 years in FY 2018 and 7.38 years in FY 2017. For information about the whistleblower claim process, see the IRS Publication 5251.
The FY 2019 annual report also reveals that there was a slight decrease in awards as a percentage of proceeds collected in FY 2019 (19.5%) compared to FY 2018 (21.7%). Notably, however, there has been a consistent increase in awards as a percentage of proceeds collected since FY 2016, which signals an increase in the quality of tips received:
- FY 2016: 16.6%
- FY 2017: 17.8%
- FY 2018: 21.7%
The FY 2019 annual report also includes, for the first time, a chart showing whistleblowers by geographic region. In the United States, the IRS received tips from whistleblowers fairly evenly throughout the country: Western Region (1,006 tips), Central Region (1,032 tips), and Eastern Region (1,320 tips). In addition, the IRS received tips from 282 whistleblowers from foreign regions, highlighting the international reach of the program.
Taxpayer First Act
On July 1, 2019, the Taxpayer First Act (TFA) was signed into law. The TFA made critical changes to protect tax whistleblowers from workplace retaliation and improve IRS communications with tax whistleblowers.
Tax Whistleblower Protection Law
The tax whistleblower protection law of the TFA prohibits any “employer, officer, employee, contractor, subcontractor, or agent” of an employer from retaliating against a whistleblower. The TFA protects a broad range of disclosures about potential violations of IRS rules or tax fraud. It protects not only disclosures to the IRS, but also internal disclosures, including an employee’s disclosure to a supervisor or “any other person working for the employer who has the authority to investigate, discover, or terminate misconduct.” A prevailing TFA whistleblower is entitled to make-whole relief, which includes:
- reinstatement;
- double back pay with interest;
- uncapped “special damages,” which courts have construed as encompassing damages for emotional distress and reputational harm; and
- attorney fees, litigation costs, and expert witness fees.
The purpose of the TFA whistleblower protection law is to encourage whistleblowers with high-value inside information about tax noncompliance to come forward. The anti-retaliation provisions will encourage whistleblowers to report large-scale tax fraud and will result in the recovery of tax underpayments which might otherwise have gone undetected. For more information on the tax whistleblower protection law, please click here.
Updates on Whistleblower Investigations
TAF also requires the IRS to provide updates to whistleblowers on the progress of the whistleblower investigation. Under Section 1405 of the TFA, the IRS Whistleblower Office must provide the following updates to tax whistleblowers:
(i) Not later than 60 days after a case for which the individual has provided information has been referred for an audit or examination, a notice with respect to such referral.
(ii) Not later than 60 days after a taxpayer with respect to whom the individual has provided information has made a payment of tax with respect to tax liability to which such information relates, a notice with respect to such payment.
(iii) Subject to such requirements and conditions as are prescribed by the Secretary, upon a written request by such individual—
(I) information on the status and stage of any investigation or action related to such information, and
(II) in the case of a determination of the amount of any award under section 7623(b), the reasons for such determination. Clause (iii) shall not apply to any information if the Secretary determines that disclosure of such information would seriously impair Federal tax administration. Information described in clauses (i), (ii), and (iii) may be disclosed to a designee of the individual providing such information in accordance with guidance provided by the Secretary.
IRS Whistleblower Reward Program
Under 26 USC § 7623(b), the IRS is required to issue an award to tax whistleblowers of 15% to 30% of proceeds collected from tax fraud or tax underpayments if:
- the whistleblower provides a tip that the IRS decides to take action on (a whistleblower cannot force the IRS to act on a tip);
- the amount in dispute (the tax underpayment, including interest and penalties) exceeds $2 million (if the taxpayer is an individual, his or her gross income must exceed $200,000 for at least one of the tax years in question); and
- the IRS collects tax underpayments resulting from the action (including any related actions).
Tax Whistleblower Awards
Since FY 2015, the IRS issued more than $611 million in awards:
- In FY 2019, the IRS issued 181 awards, totaling more than $102 million;
- In FY 2018, the IRS issued 217 awards, totaling more than $312 million;
- In FY 2017, the IRS issued 242 awards, totaling more than $33 million;
- In FY 2016, the IRS issued 418 awards, totaling more than $61 million; and
- In FY 2015, the IRS issued 99 awards, totaling more than $103 million.
For more information on the IRS Whistleblower Reward Program, click here.
IRS Whistleblower Lawyers
The whistleblower lawyers at Zuckerman Law have experience representing whistleblowers before the IRS and one of our attorneys is also a Certified Public Accountant and Certified Fraud Examiner. We are a leading whistleblower law firm and two of our attorneys were named top whistleblower lawyers in Washingtonian magazine.
U.S. News and Best Lawyers® have named Zuckerman Law a Tier 1 firm in Litigation – Labor and Employment in the Washington DC metropolitan area. Matthew Stock, the Director of the Whistleblower Rewards Practice at Zuckerman Law, has been quoted in leading publications about the IRS whistleblower program, including in Bloomberg BNA.
To discuss potential representation in a tax fraud whistleblower case with amounts in dispute of more than $2 million, click here or call us at (202) 930-5901.
What is the process to obtain an IRS whistleblower reward?